中序+后序=层序
1. 原文
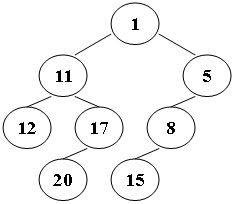
Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integers. A unique binary tree can be determined by a given pair of postorder and inorder traversal sequences. And it is a simple standard routine to print the numbers in level-order. However, if you think the problem is too simple, then you are too naive. This time you are supposed to print the numbers in “zigzagging order” – that is, starting from the root, print the numbers level-by-level, alternating between left to right and right to left. For example, for the following tree you must output: 1 11 5 8 17 12 20 15.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤30), the total number of nodes in the binary tree. The second line gives the inorder sequence and the third line gives the postorder sequence. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
output Specification:
For each test case, print the zigzagging sequence of the tree in a line. All the numbers in a line must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
1 | 8 |
Sample output:
1 | 1 11 5 8 17 12 20 15 |
2. 解析
中序 左 根 右
后序 左 右 根
1 | getLevel(int inl,int inr,int postr,int deep) |
1 | level[deep].push_back(post[postr]) |
每层递归添加
最终层按奇偶数输出
1 | printf("%d", level[1][0]); |
3. AC代码
1 |
|